Using SDK ML Python bindings
Metavision SDK provides Python bindings of the algorithms implemented in C++.
This tutorial presents:
How to load and create numpy arrays of events
How to do geometrical transformation
How to apply noise/ROI filter algorithm
How to process events to generate tensor for neural network algorithm
In the tutorial, events are set in a numpy array for the Python bindings
and visualized with matplotlib as an example.
Let’s start with some initial import that we be needed in multiple sections of this tutorial:
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [11, 7]
from metavision_sdk_core import BaseFrameGenerationAlgorithm
import metavision_sdk_ml
def are_events_equal(ev1, ev2):
"""Simple functions comparing event vector field by fields"""
return ev1.size == ev2.size and min(np.allclose(ev1[name], ev2[name]) for name in ev1.dtype.names)
Loading events
Before being able to execute algorithms from the SDK, a numpy array of CD events is required.
An empty array of events can be generated as following:
import metavision_sdk_base
empty_array = np.zeros(2, metavision_sdk_base.EventCD)
print("%r" % empty_array)
array([(0, 0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 0, 0)],
dtype={'names':['x','y','p','t'], 'formats':['<u2','<u2','<i2','<i8'], 'offsets':[0,2,4,8], 'itemsize':16})
An array of events can also be obtained by reading a RAW file or by opening an event-based camera.
To load events interactively, RawReader is used in this tutorial. The loaded events can be directly used by the different algorithms like we will see in the following sections.
Note
To process entire RAW and DAT files consider using EventsIterator
Here is the link to download the RAW file used in this sample: spinner.raw
import os
from metavision_core.event_io import RawReader
sequence_filename_raw = "spinner.raw"
Geometrical Preprocessing
Transpose
Swap x and y coordinates of an event stream.
The following code instantiates the algorithm
import metavision_sdk_cv
transpose = metavision_sdk_cv.TransposeEventsAlgorithm()
Load the events from the RAW files:
print("before transpose.process(): ")
mv_raw = RawReader(sequence_filename_raw)
ev_0_500 = mv_raw.load_delta_t(500)
print(ev_0_500)
before transpose.process():
[(237, 121, 1, 0) (246, 121, 1, 0) (248, 132, 1, 0) ...
(239, 106, 1, 499) (237, 104, 1, 499) (249, 105, 1, 499)]
Now transpose the events into a new buffer and check that the event coordinates are transposed
# Transpose without changing the input array (create a copy)
ev_0_500_transposed = transpose.get_empty_output_buffer()
transpose.process_events(ev_0_500, ev_0_500_transposed)
assert not are_events_equal(ev_0_500_transposed.numpy(), ev_0_500)
print(ev_0_500_transposed.numpy())
[(121, 237, 1, 0) (121, 246, 1, 0) (132, 248, 1, 0) ...
(106, 239, 1, 499) (104, 237, 1, 499) (105, 249, 1, 499)]
Check that the previous buffer is unchanged
print("after transpose.process(): ")
print(ev_0_500) # unchanged
after transpose.process():
[(237, 121, 1, 0) (246, 121, 1, 0) (248, 132, 1, 0) ...
(239, 106, 1, 499) (237, 104, 1, 499) (249, 105, 1, 499)]
To avoid data copy and allocation, the function process_events_()
can be used to process the events inside the provided buffer:
# Transpose in-place
transpose.process_events_(ev_0_500)
assert are_events_equal(ev_0_500_transposed.numpy(), ev_0_500)
print("After transpose.process_events_(): ")
print(ev_0_500)
After transpose.process_events_():
[(121, 237, 1, 0) (121, 246, 1, 0) (132, 248, 1, 0) ...
(106, 239, 1, 499) (104, 237, 1, 499) (105, 249, 1, 499)]
FlipX / FlipY
FlipX applies a vertical line symmetry in the middle of the image to transform all events coordinates. Whereas FlipY applies a horizontal one.
Before flipping the coordinates, let’s load some events from the file.
mv_raw = RawReader(sequence_filename_raw)
ev = mv_raw.load_delta_t(600)
print(ev)
[(237, 121, 1, 0) (246, 121, 1, 0) (248, 132, 1, 0) ...
(245, 123, 1, 599) (252, 123, 1, 599) (264, 123, 1, 599)]
Instantiate FlipX algorithm and apply it:
import metavision_sdk_core
sensor_width = mv_raw.get_size()[1]
print("sensor width: %s every x coordinate should be now x - sensor_width - 1" % sensor_width)
flipX = metavision_sdk_core.FlipXAlgorithm(sensor_width - 1)
ev_flipX_buffer = flipX.get_empty_output_buffer()
flipX.process_events(ev, ev_flipX_buffer)
print(ev_flipX_buffer.numpy())
sensor width: 640 every x coordinate should be now x - sensor_width - 1
[(402, 121, 1, 0) (393, 121, 1, 0) (391, 132, 1, 0) ...
(394, 123, 1, 599) (387, 123, 1, 599) (375, 123, 1, 599)]
Instantiate FlipY algorithm and apply it:
sensor_height = mv_raw.get_size()[0]
print("sensor height: %s every y coordinate should be now y - sensor_height - 1" % sensor_height)
flipY = metavision_sdk_core.FlipYAlgorithm(sensor_height - 1)
ev_flipY_buffer = flipY.get_empty_output_buffer()
flipY.process_events(ev, ev_flipY_buffer)
print(ev_flipY_buffer.numpy())
sensor height: 480 every y coordinate should be now y - sensor_height - 1
[(237, 358, 1, 0) (246, 358, 1, 0) (248, 347, 1, 0) ...
(245, 356, 1, 599) (252, 356, 1, 599) (264, 356, 1, 599)]
As for the transpose algorithm, the buffer can be processed in place
with the function process_events_()
flipX.process_events_(ev)
flipY.process_events_(ev)
print(ev)
[(402, 358, 1, 0) (393, 358, 1, 0) (391, 347, 1, 0) ...
(394, 356, 1, 599) (387, 356, 1, 599) (375, 356, 1, 599)]
Event filtering
Region Of Interest (ROI)
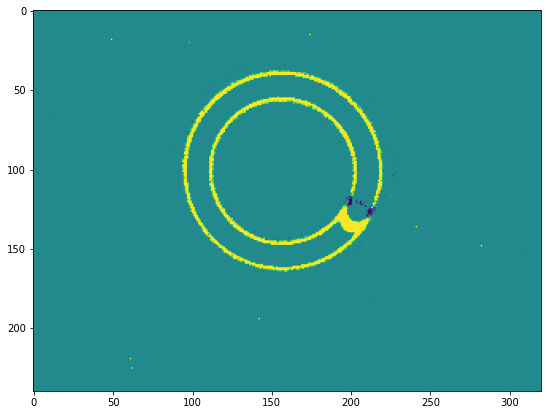
The Region Of Interest Algorithm filters out all events that are outside of a rectangular region of interest. The filter takes two coordinates as arguments: one coordinate per rectangle corner (the top left and the right bottom corners).
In the following code, the RoiFilter is instantiated to remove all events outside of a box represented by its corners coordinates:
top left: (200, 100);
bottom right: (320, 200).
roi = metavision_sdk_core.RoiFilterAlgorithm(x0=100, y0=255, x1=200, y1=320)
ev_filtered_buffer = roi.get_empty_output_buffer()
mv_raw = RawReader(sequence_filename_raw)
ev = mv_raw.load_delta_t(1000000)
roi.process_events(ev, ev_filtered_buffer)
ev_filtered = ev_filtered_buffer.numpy()
print(ev_filtered)
[(200, 255, 0, 39383) (199, 256, 0, 39563) (199, 257, 0, 39642)
(200, 256, 0, 39812) (200, 255, 1, 40637) (200, 256, 1, 40906)
(200, 255, 1, 45862) (199, 257, 1, 48041) (199, 256, 1, 49813)
(168, 276, 1, 57907) (200, 255, 0, 91052) (200, 255, 1, 92190)
(200, 255, 1, 95971) (200, 255, 0, 142297) (200, 257, 0, 142483)
(200, 257, 1, 143130) (200, 255, 1, 143297) (200, 255, 1, 144263)
(200, 257, 1, 150707) (199, 256, 0, 193488) (199, 255, 0, 193532)
(200, 255, 0, 193532) (200, 255, 1, 194456) (199, 255, 1, 194726)
(199, 256, 1, 195258) (200, 255, 1, 195682) (200, 255, 0, 244590)
(200, 256, 0, 244744) (200, 255, 1, 245456) (200, 256, 1, 245638)
(200, 255, 1, 246414) (168, 276, 1, 274040) (200, 255, 0, 346822)
(200, 255, 1, 347796) (200, 255, 1, 349733) (200, 260, 0, 397437)
(200, 255, 0, 448336) (200, 256, 0, 448614) (200, 255, 1, 449585)
(200, 256, 1, 449687) (200, 255, 1, 451222) (168, 276, 1, 493086)
(200, 255, 0, 499009) (199, 255, 0, 499236) (200, 255, 1, 499954)
(199, 255, 1, 500099) (200, 255, 1, 501250) (200, 255, 0, 549545)
(200, 255, 1, 550343) (200, 255, 1, 551241) (200, 255, 0, 600059)
(200, 256, 0, 600117) (200, 255, 1, 600953) (200, 256, 1, 601383)
(200, 255, 1, 601669) (200, 255, 0, 650974) (200, 255, 1, 651580)
(200, 255, 1, 652548) (200, 255, 0, 702101) (199, 257, 0, 702141)
(199, 256, 0, 702163) (199, 255, 0, 702236) (200, 255, 1, 703133)
(199, 255, 1, 703525) (199, 256, 1, 705486) (200, 255, 1, 708863)
(168, 276, 1, 724152) (200, 255, 0, 753381) (200, 255, 1, 754647)
(200, 255, 1, 766320) (200, 255, 0, 805017) (200, 256, 0, 805157)
(200, 257, 0, 805227) (200, 257, 1, 805858) (200, 255, 1, 806272)
(200, 256, 1, 806573) (200, 257, 1, 807594) (200, 255, 1, 816322)
(200, 255, 0, 856302) (199, 256, 0, 856483) (200, 258, 0, 856568)
(200, 255, 1, 857654) (199, 256, 1, 858683) (200, 258, 1, 861174)
(200, 255, 1, 862778) (168, 276, 1, 906007) (200, 255, 0, 907439)
(199, 255, 0, 907757) (200, 255, 1, 908709) (199, 255, 1, 908916)
(200, 255, 1, 915395) (200, 255, 0, 958662) (200, 255, 1, 959941)
(200, 255, 1, 962044)]
To show that all the events are in the provided ROI is easier to check with an image:
height, width = mv_raw.get_size()
frame = np.zeros((height, width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
BaseFrameGenerationAlgorithm.generate_frame(ev_filtered, frame)
image = plt.imshow(frame[..., ::-1])

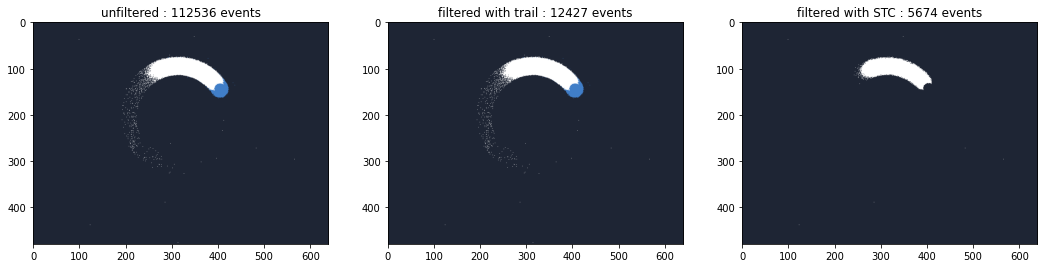
Noise Filters: Trail / STC
Trail and STC filters are used to reduce the number of events produced by the camera.
First, load some events.
mv_raw = RawReader(sequence_filename_raw)
height, width = mv_raw.get_size()
mv_raw.seek_time(2e6)
ev = mv_raw.load_delta_t(10000)
Instantiate the noise filtering algorithms and apply them on the buffer of events
trail = metavision_sdk_cv.TrailFilterAlgorithm(width=width, height=height, threshold=10000)
ev_trail_buf = trail.get_empty_output_buffer()
trail.process_events(ev, ev_trail_buf)
ev_trail_np = ev_trail_buf.numpy()
stc = metavision_sdk_cv.SpatioTemporalContrastAlgorithm(width=width, height=height, threshold=10000)
ev_stc_buf = stc.get_empty_output_buffer()
stc.process_events(ev, ev_stc_buf)
ev_stc_np = ev_stc_buf.numpy()
To compare the behavior of the algorithms, the generated frames are displayed side by side with the number of events
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [18, 7]
_, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(1, 3)
ax1.set_title("unfiltered : {} events".format(len(ev)))
BaseFrameGenerationAlgorithm.generate_frame(ev, frame)
ax1.imshow(frame[..., ::-1])
ax2.set_title("filtered with trail : {} events".format(len(ev_trail_np)))
BaseFrameGenerationAlgorithm.generate_frame(ev_trail_np, frame)
ax2.imshow(frame[..., ::-1])
ax3.set_title("filtered with STC : {} events".format(len(ev_stc_np)))
BaseFrameGenerationAlgorithm.generate_frame(ev_stc_np, frame)
image = ax3.imshow(frame[..., ::-1])
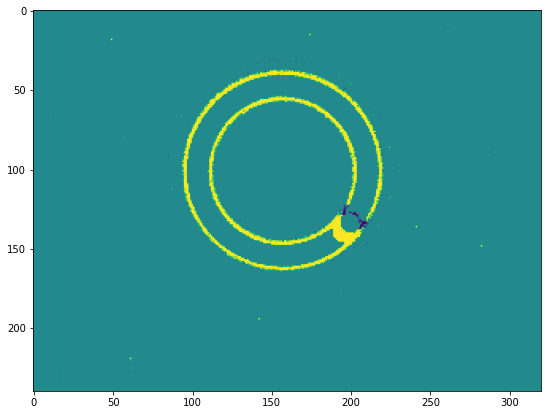
Event preprocessing : CDProcessing
CDProcessing is a C++ implementation of the function described in the event preprocessing tutorial.
# the visualization functions from metavision_ml can be used.
from metavision_ml.preprocessing import viz_histo
We create a CDProcessing function with:
histodelta_t = 50ms
network input size as a half of the size of the event_frame
mv_raw = RawReader(sequence_filename_raw)
height, width = mv_raw.get_size()
mv_raw.seek_time(3e6)
ev = mv_raw.load_delta_t(50000)
cdproc = metavision_sdk_ml.CDProcessing.create_CDProcessingHisto(delta_t=50000,
network_input_width=width // 2,
network_input_height=height // 2,
event_input_width=width, event_input_height=height)
frame_buffer = cdproc.init_output_tensor()
cdproc.process_events(3000000, ev, frame_buffer)
print("frame_buffer shape : ", frame_buffer.shape)
print("number of non-zero values : ", np.sum(frame_buffer != 0))
print("set of unique values :\n", np.around(np.unique(frame_buffer), decimals=2))
plt.imshow(viz_histo(frame_buffer))
frame_buffer shape : (2, 240, 320)
number of non-zero values : 13572
set of unique values :
[0. 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65
0.7 0.75 0.8 0.85 0.9 0.95 1. ]
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7fbc16770320>

ev = mv_raw.load_delta_t(50000)
# reset and reuse the frame_buffer
frame_buffer.fill(0)
cdproc.process_events(3050000, ev, frame_buffer)
print("frame_buffer shape : ", frame_buffer.shape)
print("number of non-zero values : ", np.sum(frame_buffer != 0))
print("set of unique values :\n", np.around(np.unique(frame_buffer), decimals=2))
plt.imshow(viz_histo(frame_buffer))
frame_buffer shape : (2, 240, 320)
number of non-zero values : 13594
set of unique values :
[0. 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65
0.7 0.75 0.8 0.85 0.9 0.95 1. ]
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7fbc1675b320>